Global sensitivity analysis of n-butanol reaction kinetics using rate rules

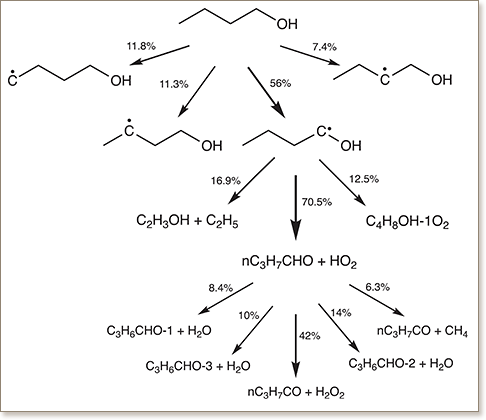
We investigate the sensitivity of the ignition delay time, τign, of n-butanol to uncertainties in the rate-rule kinetic rate parameters, at various initial temperatures (600–1000 K), pressures (10–80 bar) and equivalence ratios (0.5–2.0). We start by considering a 30-dimensional stochastic germ in which each random variable is associated with one reaction class, and build a surrogate model for the ignition delay time using polynomial chaos expansions. The adaptive pseudo-spectral projection technique is used for this purpose. The surrogate model is used to estimate first-order and total-order sensitivity indices characterizing the dependence of the ignition delay time on the uncertain inputs. Results indicate that τign is mostly sensitive to variations in four dominant reaction classes, namely, H–atom abstraction from the fuel (reaction class 2), addition of O2 to the fuel radicals (reaction class 11), fuel radical isomerization including Waddington type reactions (reaction class 15), and concerted elimination reactions (reaction class 16). We consequently focus our attention on these four reaction classes, and consider variations within corresponding subrules. We explore two approaches to define the subrules of reaction class 2, one based on the radical abstracting from the fuel resulting in eleven subrules and another based on the abstraction site resulting in five subrules. Hence, we investigate the sensitivity of τign due to variability in the rate parameters of 26 and 20 subrules of the resulting models. In particular, the simulations indicate that in reaction class 2 H–atom abstraction by HO2 dominates the variability in τign at all initial conditions considered. Analysis of this finding reveals that correlations inherent in the rate rule construction plays an important role in the resulting sensitivity predictions, and suggests a hierarchical approach to the calibration of elementary reaction rates.
DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2018.06.035

"KAUST shall be a beacon for peace, hope and reconciliation, and shall serve the people of the Kingdom and the world."
King Abdullah bin Abdulaziz Al Saud, 1924 – 2015
Thuwal 23955-6900, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
© King Abdullah University of Science and Technology. All rights reserved